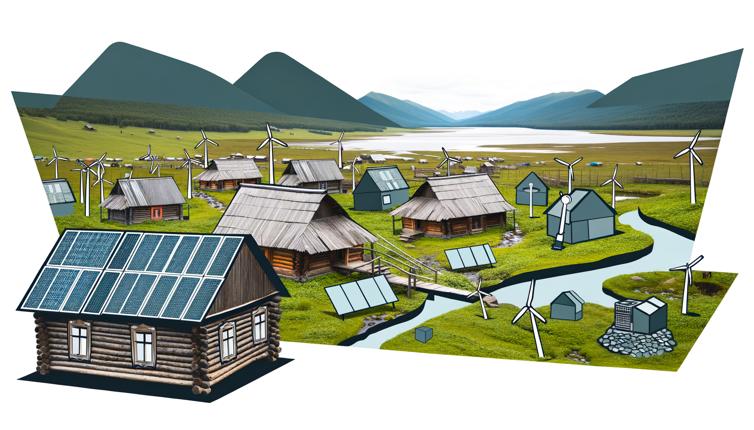
Solar Power
Solar power is one of the most popular and widely used alternative energy sources for remote areas. It harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity through the use of photovoltaic panels. The panels capture sunlight and convert it into usable electricity, which can power homes, schools, clinics, and other essential facilities.,Solar power offers several advantages in remote areas. First, it is a renewable energy source, meaning it does not deplete natural resources. This makes it a sustainable option for long-term energy needs. Second, solar power systems are relatively easy to install and maintain, making them suitable for remote locations where technical expertise may be limited. Lastly, solar power can be used to charge batteries, providing a backup power source when sunlight is not available.,However, there are some challenges associated with solar power in remote areas. The initial cost of installing solar panels and associated equipment can be high, making it unaffordable for some communities. Additionally, solar power generation relies on sunlight, so areas with limited sunlight or frequent cloudy weather may not benefit fully from this energy source.
Wind Power
Wind power is another alternative energy source that can be harnessed in remote areas. It utilizes the energy of wind to produce electricity through wind turbines. These turbines have large blades that spin when the wind blows, generating kinetic energy that is converted into electrical energy.,Wind power has several advantages in remote areas. First, wind is a free and abundant resource in many remote locations, providing a consistent energy source. Second, wind power is environmentally friendly, producing zero emissions and helping to reduce carbon footprints. Lastly, wind turbines can be installed in remote areas, including offshore locations, making it possible to generate power in areas without access to traditional electricity grids.,However, wind power also has its challenges. The installation and maintenance of wind turbines require specific technical expertise, which may not be readily available in remote areas. Additionally, wind power generation can be affected by factors such as wind speed and direction, so careful site selection is crucial for maximizing power generation.
Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power harnesses the energy of flowing or falling water to generate electricity. It involves the construction of dams or diversion structures to create a reservoir of water. When the water is released, it flows through turbines, which spin to generate electricity.,Hydroelectric power offers several benefits in remote areas. First, it is a reliable and consistent energy source, as the flow of water is generally predictable. Second, hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source, as water is constantly replenished by natural processes such as rainfall. Lastly, hydroelectric power plants can also offer additional benefits, such as water storage for irrigation purposes or flood control.,However, hydroelectric power may not be suitable for all remote areas. It requires access to a water source with sufficient flow and elevation difference, which may limit its applicability. Additionally, the construction of hydroelectric power plants can have significant environmental impacts, such as altering the natural flow of rivers and disrupting ecosystems.
Conclusion
Alternative energy sources play a crucial role in providing power to remote areas where traditional energy sources may be limited. Solar power, wind power, and hydroelectric power are just a few examples of the alternative energy sources that can be harnessed in these areas. Each source has its advantages and challenges, and the suitability depends on factors such as resource availability and technical expertise. By leveraging these alternative energy sources, remote communities can improve their quality of life, access essential services, and contribute to a more sustainable future.