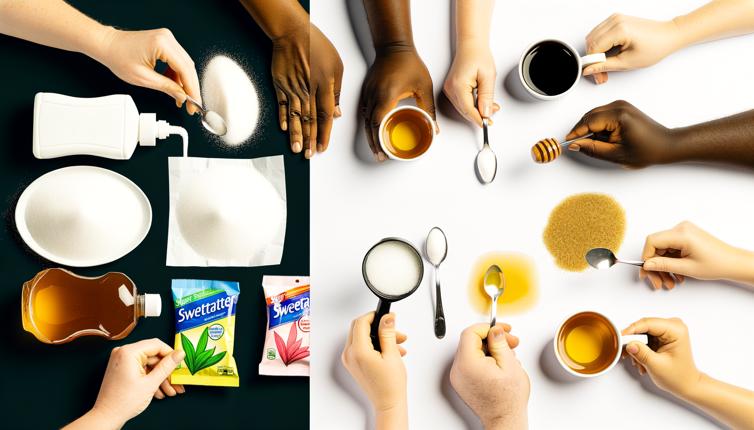
Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners are synthetic sugar substitutes that are designed to mimic the taste of sugar without the added calories. They are commonly used in a wide range of food and beverage products, including diet soda, low-calorie snacks, and sugar-free desserts. Some examples of artificial sweeteners include aspartame, saccharin, sucralose, and acesulfame potassium.,One of the main benefits of artificial sweeteners is their low caloric content, which makes them attractive to individuals trying to lose weight or manage diabetes. These sweeteners have a much higher sweetness intensity compared to sugar, allowing a smaller amount to be used to achieve the same level of sweetness. This can help reduce overall calorie intake and lower the risk of developing conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.,However, there are also potential risks associated with the consumption of artificial sweeteners. Some studies suggest that artificial sweeteners may disrupt the body's natural ability to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to increased cravings for sweet foods and potentially contributing to weight gain. Additionally, long-term consumption of artificial sweeteners has been linked to a higher risk of metabolic syndrome, which is a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.,It is important to note that the safety of artificial sweeteners is regulated by health authorities, and they are considered safe for consumption within recommended limits. However, it is advisable to consume them in moderation and to opt for natural alternatives when possible.
Natural Alternatives
Natural alternatives to artificial sweeteners include a variety of plant-based sweeteners that are derived from natural sources such as fruits, vegetables, and herbs. These sweeteners are often marketed as healthier alternatives to sugar and artificial sweeteners, as they are less processed and may contain additional nutrients.,Stevia is one of the most well-known natural sweeteners and is extracted from the leaves of the stevia plant. It is calorie-free and has been used for centuries in South America as a natural sweetener. Other examples of natural sweeteners include monk fruit extract, coconut sugar, and honey.,One of the main advantages of natural alternatives is that they are generally considered to be safe and have a lower risk of potential health effects compared to artificial sweeteners. Many natural sweeteners also have a lower glycemic index, meaning they have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels. This can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those looking to reduce their sugar intake.,However, it is important to remember that natural sweeteners are still a form of sugar and should be consumed in moderation. They may still contribute to calorie intake and can have similar effects on the body as regular sugar if consumed in excessive amounts.,In conclusion, sugar substitutes offer a range of options for individuals looking to reduce their sugar intake or manage conditions such as diabetes or obesity. Artificial sweeteners provide a low-calorie alternative to sugar, but their long-term health effects are still a topic of debate. Natural alternatives, on the other hand, offer a potentially healthier option, but they should still be consumed in moderation. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet.
Conclusion
Decoding the world of sugar substitutes requires a thorough understanding of both artificial sweeteners and natural alternatives. While artificial sweeteners can provide a low-calorie alternative to sugar, their potential health risks must be taken into consideration. Natural alternatives offer a potentially healthier option, but moderation is still key. Ultimately, finding the right balance and personalized approach to sugar substitutes is important for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.